🇮🇳 India’s Poverty Reduction: Key Highlights & Investment Insights (2025)
📌 Global Revision: New Poverty Line
The World Bank has raised the International Poverty Line (IPL) from $2.15/day (2017 PPP) to $3.00/day (2021 PPP).
Global extreme poverty count increased by 125 million.
India emerged as an outlier, reducing its poverty count by 125 million, thanks to refined data and updated survey methods.
India’s adoption of updated consumption data and methodology significantly influenced the global poverty recalibration.
📊 Revised Poverty Statistics: Before vs After
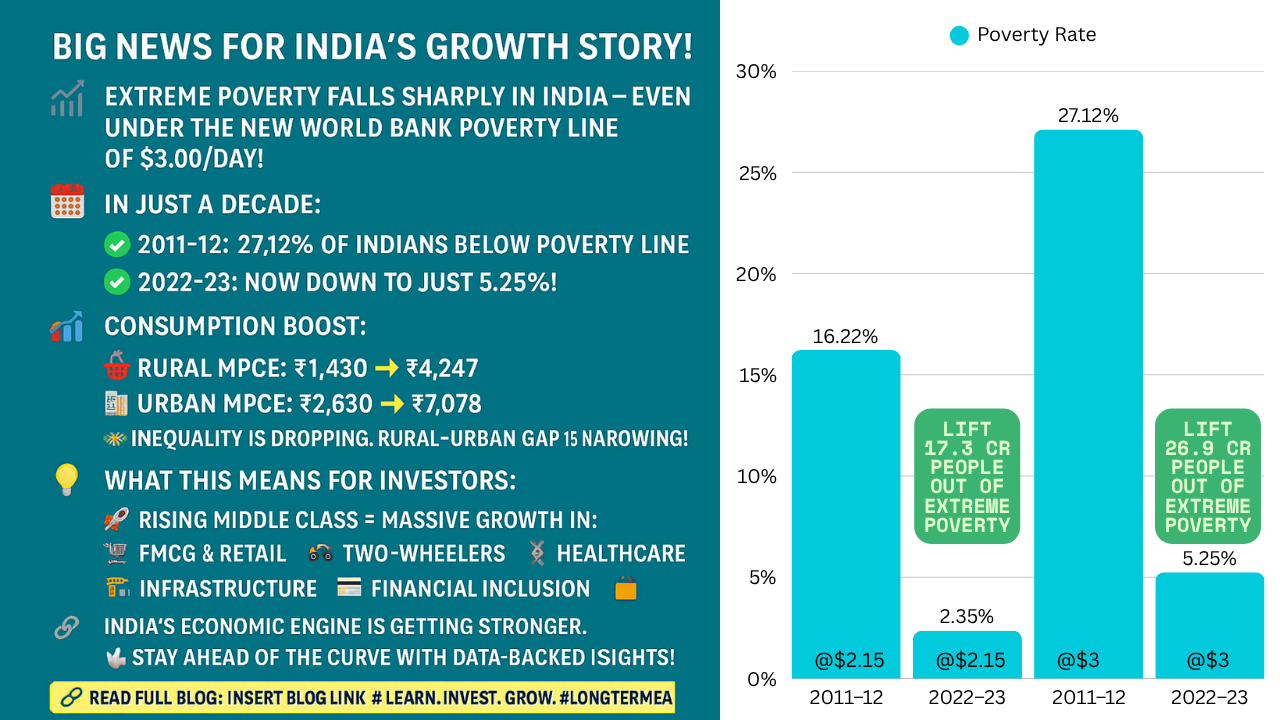
🔍 Insight: Even with a higher threshold, India has drastically reduced poverty — a fall from 27.12% to 5.25% in just over a decade.
🏡 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023–24
📌 MPCE = Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure
📉 Consumption Inequality (Gini Coefficient):
Rural: ↓ from 0.266 to 0.237
Urban: ↓ from 0.314 to 0.284
📈 Top State-Wise Gain:
Odisha recorded the highest rural MPCE increase (~14%)
🔎 Investor-Relevant Implications
✅ 1. Long-Term Consumption Boom
With higher MPCE, India is witnessing an expanding middle class and increased disposable income, benefiting:
FMCG & Consumer Staples
Retail & E-commerce
Discretionary Products
Automobiles & Consumer Durables
✅ 2. Rural Demand Resurgence
Rising rural consumption and reduced inequality = rural market expansion for:
Consumer durables
Two-wheelers
Affordable healthcare & education
Agri-inputs and allied services
Key Beneficiaries:
Consumer Staples & Discretionary: Boost in everyday spending and aspirational products
Retail & E-commerce: Wider rural adoption and spending
Automobiles: Entry-level vehicle sales to see strong traction
Agriculture & Allied Sectors: Higher rural income → investment in productivity
Financial Services (Rural Focus): Greater credit and insurance demand
✅ 3. Financial Inclusion & Credit Growth
As poverty declines:
Credit quality improves
Lending expands
📈 Sectors to benefit:
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
NBFCs
Small Finance Banks
✅ 4. Policy Stability & Capex Continuity
India’s progress is backed by:
Evidence-based governance
Reform-driven initiatives
⛳ Continued investment in:
Infrastructure
Rural development
Social welfare schemes
🏗️ Investment-worthy Sectors:
Capital Goods & Construction
Infra Developers
Rural Fintech & Agri-tech
🧠 Conclusion: Measurement + Momentum = Market Opportunity
India’s story is a model of transformation:
📈 Better data + Strong policy = Real growth
This shift lays the foundation for long-term investment opportunities across sectors — from rural consumption to infrastructure and financial services.

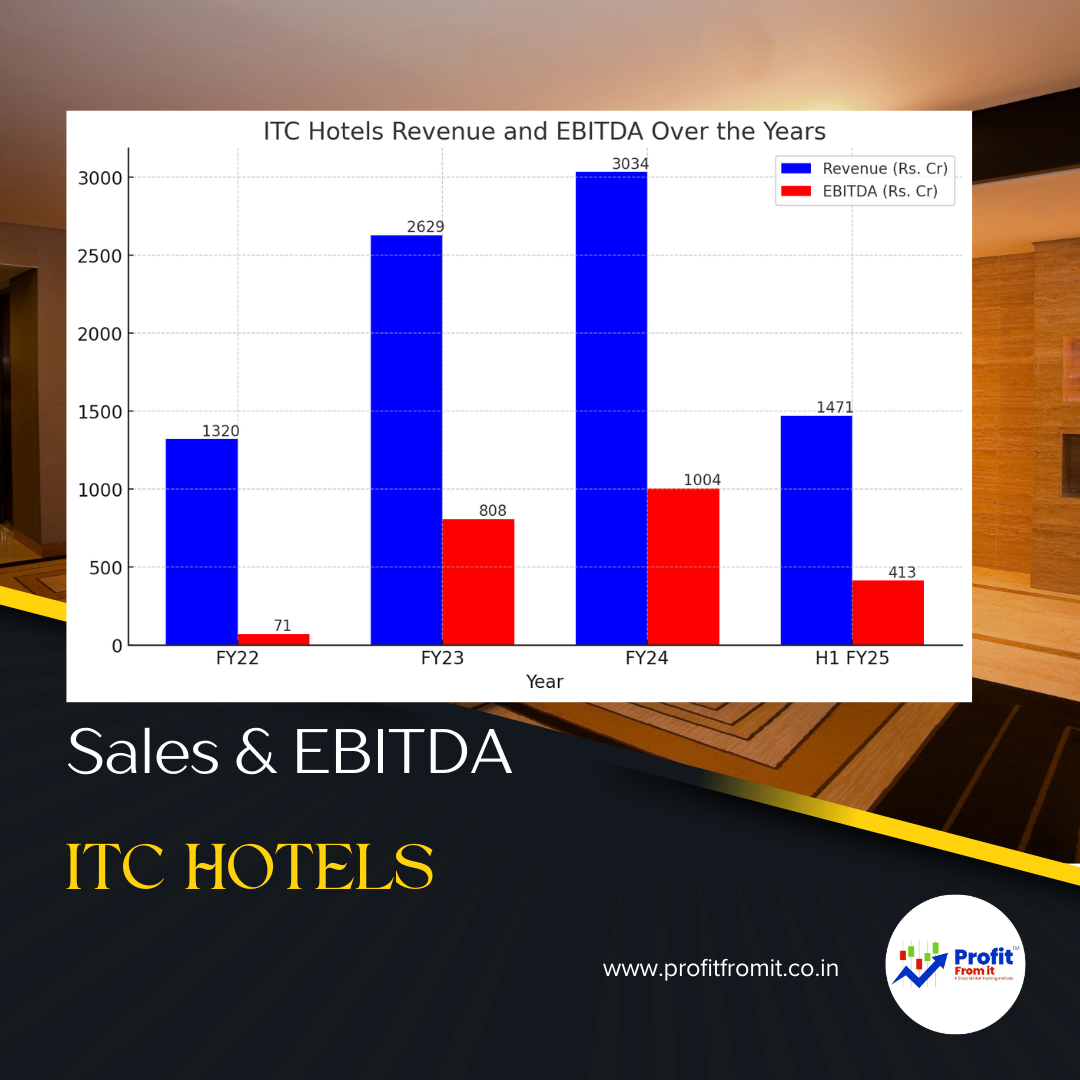

 for Investors The provided chart outlines key metrics for Nifty 500 companies across different periods (FY22 t.png)