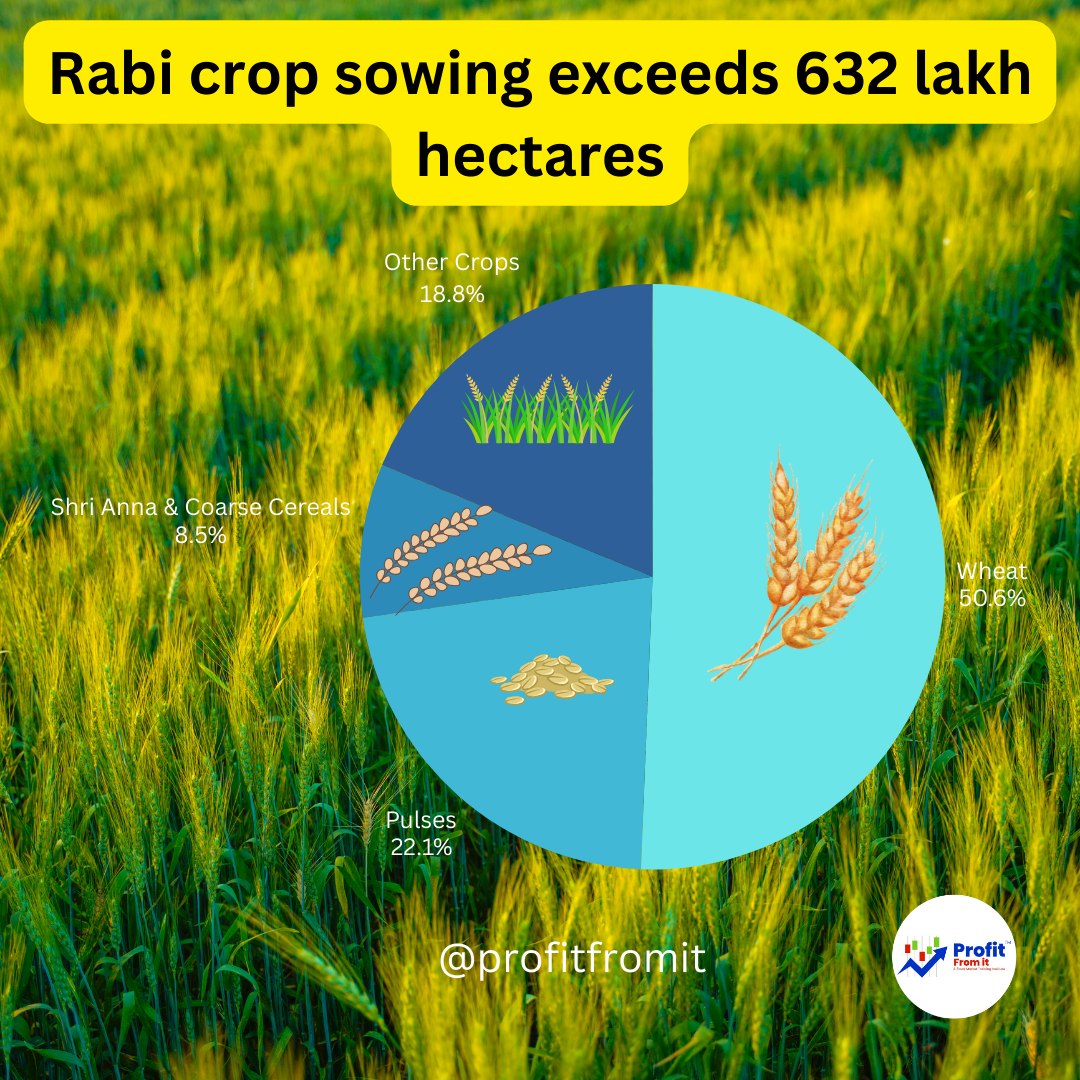
Current sowing area for various Rabi crops as compared to the previous year, which can have several direct and indirect effects on different sectors due to their role as raw materials in various industries:
Direct Impact on Sectors:
Agriculture & Farming Equipment 🚜: Increased area under crops like wheat, pulses, and oilseeds suggests a higher demand for farming inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides. This also potentially increases the demand for agricultural machinery like tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems.
Food Processing 🥖:
Wheat 🌾: A staple in many diets, an increase in wheat production affects flour mills and bakeries directly.
Pulses 🌿: Higher sowing of pulses can benefit the dal milling industry and manufacturers of packaged pulse products.
Oilseeds 🌻: Increased production of oilseeds like mustard, groundnut, and sesame affects the edible oil processing industry.
Textiles 🧵:
Crops like cotton, although not mentioned specifically in your data, are similarly affected in terms of textile industries when their production levels change.
Indirect Impact on Sectors:
Retail & Consumer Goods 🛒: Increased production of essential commodities like wheat and oilseeds can lead to stabilized or reduced prices for consumer goods, potentially increasing consumer spending power in other areas.
Transport & Logistics 🚚: Higher production levels necessitate enhanced logistics for storage and distribution, impacting the transport sector.
Banking & Financial Services 🏦: With increased production, there might be a higher demand for crop loans and insurance products, benefiting the banking and financial services sectors.
Energy & Fuel ⛽: Agriculture is an energy-intensive industry. Increased cultivation areas can lead to higher fuel consumption for farm equipment and transport vehicles.
Technology & Automation 🖥️: As farms expand, there’s a growing trend toward using technology for efficient farm management systems, including software for crop management, automated irrigation systems, and satellite imaging.
Economic Effects:
Increased agricultural output can contribute to economic stability in rural areas, impacting national food security and trade balances. However, overproduction can also lead to price drops, which while beneficial for consumers, may negatively affect farmers' incomes.
This analysis offers a broad overview based on the specific crop sowing data and general knowledge of associated industries. For a more detailed impact analysis, additional data such as regional sowing patterns, yield estimates, and market prices would be beneficial.
Comments (0)
Categories
Recent posts

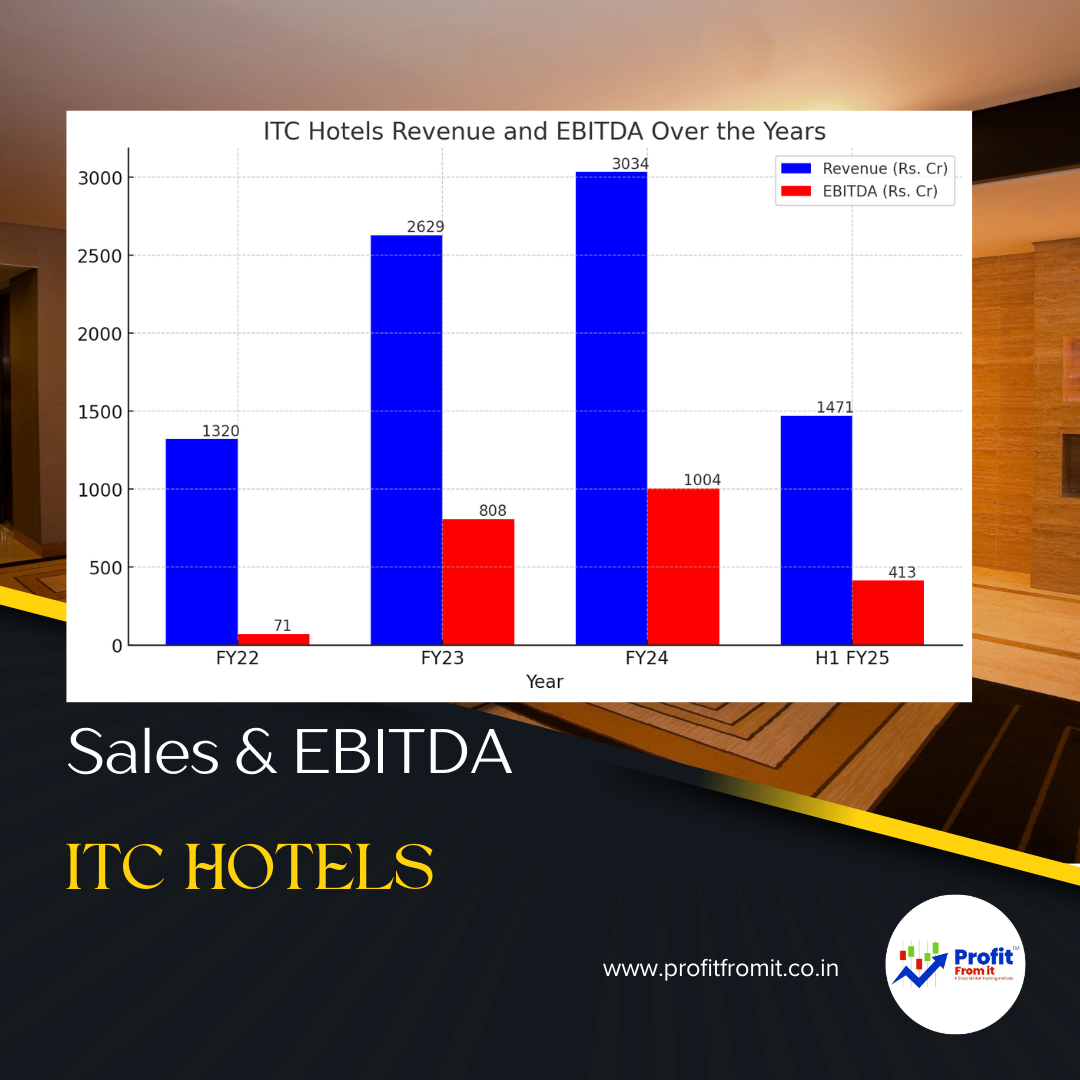
ITC Hotels and its strategic plans ...
30 Dec 2024
Reliance Leads Energy Revolution: 100% ...
22 Jan 2025 for Investors The provided chart outlines key metrics for Nifty 500 companies across different periods (FY22 t.png)
📊 Analysis of Nifty 500 Companies: ...
14 Feb 2025




