Inflation, Liquidity, and Market Moves: RBI’s Playbook for 2025:
Based on the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) statements and reports from February 2025, here’s an analysis of key monetary policy decisions, economic indicators, and their impact on the stock market.
1. Key Monetary Policy Decisions
Repo Rate Cut: The RBI reduced the policy repo rate by 25 basis points (bps) from 6.50% to 6.25%. Consequently:
Standing Deposit Facility (SDF): Adjusted to 6.00%.
Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) & Bank Rate: Adjusted to 6.50%.
Monetary Policy Stance: Continued with a neutral stance, focusing on:
Supporting economic growth.
Ensuring inflation remains aligned with the 4% target (±2%).
Implication on Stock Markets
Rate cuts typically boost equity markets as borrowing costs decline, making credit cheaper for businesses and consumers.
Interest rate-sensitive sectors like banking, real estate, and infrastructure could see a positive impact.
Lower rates may encourage higher corporate earnings and increased stock market participation.
2. Growth Outlook
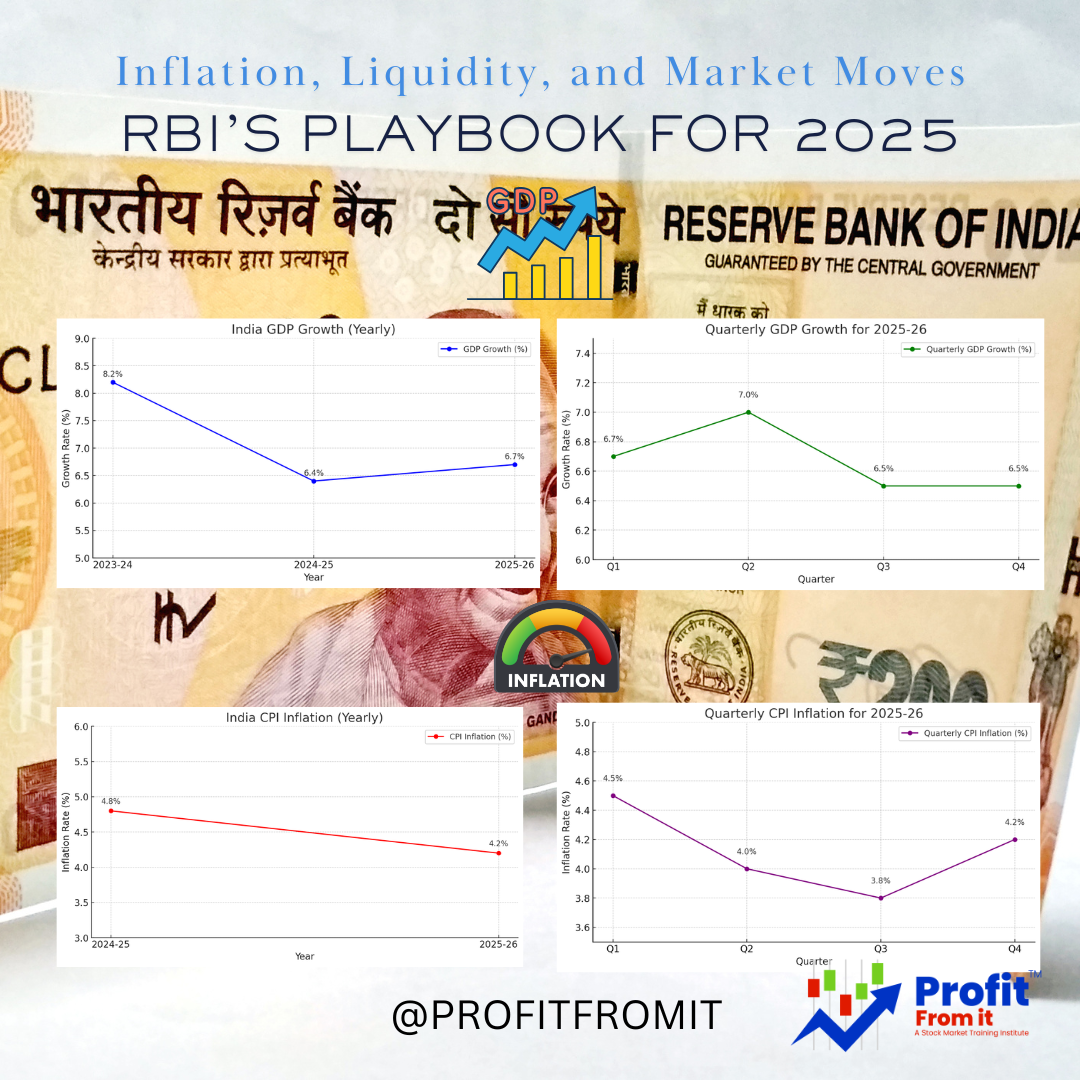
Current Fiscal Year (2024-25): GDP growth estimated at 6.4% (YoY), lower than the 8.2% growth last year.
Next Fiscal Year (2025-26): GDP growth projected at 6.7%.
Q1: 6.7%, Q2: 7.0%, Q3 & Q4: 6.5%.
Growth drivers:
Recovery in Private Consumption.
Strong Rabi Crop Prospects due to higher reservoir levels and sowing acreage.
Gradual industrial recovery expected in H2 of 2024-25.
Government’s continued capital expenditure is expected to fuel investment.
Risks to Growth:
Global geopolitical tensions, protectionist trade policies, and financial market volatility.
Slowdown in global growth (projected at 3.3% for 2025-26, below the historical 3.7%).
Stock Market Implications
Higher growth prospects are positive for stock markets, especially for consumer-driven sectors (FMCG, retail, autos).
Strong capital expenditure spending supports infrastructure and manufacturing stocks.
A weaker-than-expected industrial recovery could impact cyclical sectors like metals and capital goods.
3. Inflation Outlook
Current Fiscal Year (2024-25): CPI inflation projected at 4.8%, with Q4 at 4.4%.
Next Fiscal Year (2025-26): Inflation projected at 4.2%:
Q1: 4.5%, Q2: 4.0%, Q3: 3.8%, Q4: 4.2%.
Food Inflation: Expected to soften due to:
Good Kharif production.
Winter easing of vegetable prices.
Favorable Rabi crop prospects.
Risks to Inflation:
Energy price volatility (crude oil fluctuations).
Global market uncertainties and weather-related disruptions.
Stock Market Implications
Moderating inflation supports RBI’s rate cuts, making the stock market attractive.
Lower inflation boosts consumer spending, benefiting retail, FMCG, and discretionary consumption stocks.
If inflation surprises on the upside, it could trigger bond yield increases, impacting banking and financials.
4. Liquidity and Financial Market Conditions
Liquidity Deficit: System liquidity turned into deficit in Dec 2024 & Jan 2025, mainly due to:
Advance tax payments.
Capital outflows.
RBI's forex market interventions.
Bank Credit Growth: Registered 12.5% growth (YoY), with deposit growth at 10.6%.
System Stability: Banking sector remains healthy, with a Credit-Deposit Ratio (CDR) at 80.8%.
Stock Market Implications
Liquidity tightening may limit rapid market gains.
Strong banking fundamentals are positive for financial stocks.
RBI’s interventions to ensure liquidity stability could calm bond markets, supporting equities.
5. External Sector & Exchange Rate
Current Account Deficit (CAD): Moderated to 1.2% of GDP in Q2 2024-25, expected to remain within sustainable levels.
Rupee Depreciation: INR depreciated 3.2% against the US dollar (Nov 2024 - Jan 2025).
Forex Reserves: Stand at $630.6 billion, covering 10+ months of imports.
Stock Market Implications
Weak INR benefits export-driven stocks (IT, Pharma).
High forex reserves provide economic stability, reducing risk for foreign investors.
Continued capital outflows could cause volatility in FII-heavy sectors like financials and IT.
6. Additional Announcements Impacting Financial Markets
Digital Security Measures:
"Bank.in" exclusive domain for Indian banks to prevent fraud.
Two-factor authentication for online international payments.
Interest Rate Derivatives: Introduction of forward contracts in Govt securities to help institutional investors.
Increased Market Access: Non-bank brokers (SEBI-registered) will gain access to RBI’s government securities trading platform (NDS-OM).
Potential Review of Market Trading Timings: RBI to assess whether market hours need adjustment.
Stock Market Implications
Improved digital security reduces fraud risk, helping fintech and banking stocks.
More accessible government securities trading benefits bond market liquidity.
Potential changes in market trading hours could impact high-frequency trading (HFT) strategies and derivatives markets.
Conclusion: What This Means for the Stock Market
Positive Factors:
✅ Lower interest rates → Boosts banking, real estate, and consumption sectors.
✅ Moderating inflation → Encourages equity investments, benefits FMCG, auto, and consumer stocks.
✅ Stronger economic growth (6.7% in 2025-26) → Positive for cyclical sectors (infra, capital goods).
✅ High forex reserves and stable CAD → Enhances market confidence, supporting FII inflows.
Risk Factors:
⚠️ Global uncertainties (geopolitics, US Fed rate decisions) → Could trigger market volatility.
⚠️ Liquidity pressures → Banks facing funding constraints could impact credit growth.
⚠️ Fluctuating crude oil prices → Could hurt energy-dependent sectors (transport, logistics).
Investment Strategy in Light of RBI's Policy
Sectors to Watch:
🔹 Banking & NBFCs: Lower rates → Margin pressure, but credit growth supports stocks.
🔹 Infrastructure & Real Estate: Lower cost of borrowing → Boosts housing demand & infra projects.
🔹 Consumption (FMCG, Auto, Retail): Lower inflation + tax relief → Stronger demand.
🔹 IT & Pharma: INR depreciation → Supports export-driven earnings.
Caution for:
❌ Energy & Commodities: If oil prices surge, input costs could erode margins.
❌ Import-heavy sectors: INR depreciation increases raw material costs.
Final Takeaway
RBI’s rate cut and neutral stance signal pro-growth policies, which are generally positive for the stock market. However, global uncertainties and liquidity concerns require a balanced approach to investing.
Short-Term Outlook:
📈 Stock market bullish on rate cut, banking, infra, and consumption sectors to benefit.
📉 Watch for global risks, crude oil volatility, and potential liquidity constraints.
