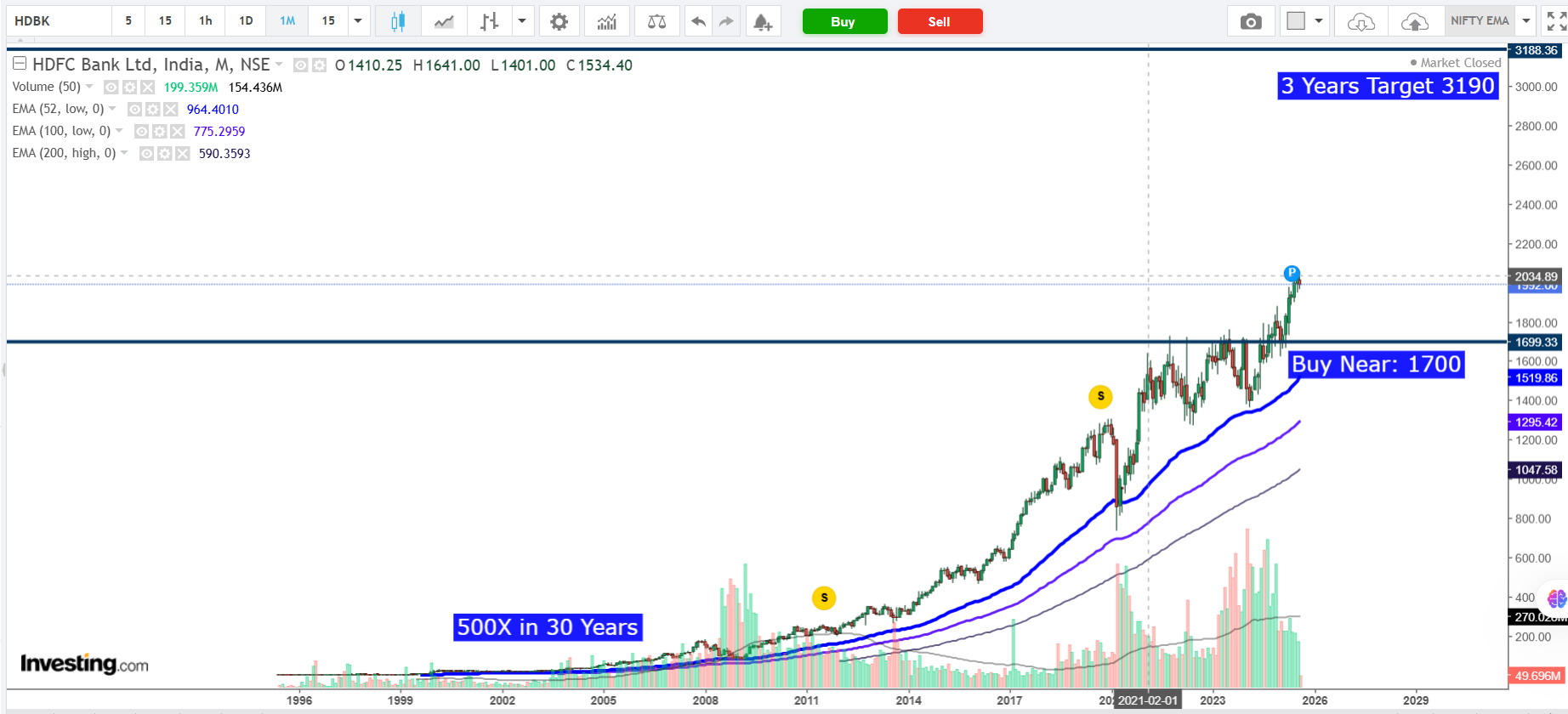
🏦 HDFC Bank – India’s Leading Private Sector Bank & Long-Term Wealth Compounder
📌 Company Overview
Founded in 1994, HDFC Bank has grown from a small private lender into India’s largest private sector bank by market capitalization, driven by its consistent growth in advances, deposits, fee income, and a robust risk management framework. Following its merger with HDFC Ltd. in FY2024, the bank has significantly expanded its loan book, diversified into housing finance, and strengthened cross-sell capabilities across insurance, asset management, and investment services.
🌏 Fairvalue:
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/e/2PACX-1vRg1tSKFe-u3gKrsjyojpraa0BgCp8uc91CDC5EW5wLCHb_RJ8_6sbNVHNBNtQ6Ww/pubhtml?gid=1098740149&single=true
🌏 Industry Overview
India’s banking sector is poised for steady growth due to:
Rising credit penetration and formalization of the economy 📈
Strong GDP growth supporting loan demand
Expanding retail credit market in housing, vehicle, and unsecured segments
Digital adoption accelerating cost efficiencies and customer reach
Private sector banks like HDFC Bank benefit from superior asset quality, strong liability franchise, and technological leadership.
📈 Historical Growth – Advances, Revenue, and Profits
*Adjusted for splits, †Merger with HDFC Ltd.
🚀 25-Year CAGR:
Advances: 31%
Revenue: 28%
Net Profit: 29%
EPS: 22%
🛡 Asset Quality – GNPA (%) History
From FY2008 onward, GNPA ratios have remained among the lowest in the industry:
Peak GNPA: 2.0% in FY2009 (global financial crisis)
Current GNPA: 1.4% (TTM FY26) – marginal increase due to macro headwinds and merger impact.
📊 Valuation Bands – PE & PBV History
P/E: Historically ranged 15x–28x, with long-term average near 21x.
P/BV: Historically ranged 2.3x–4.8x, with post-merger consolidation bringing PBV closer to 2.5–2.9x.
🆕 Latest Q1 FY26 Performance
Revenue: ₹1,33,054 Cr (↑ 13.7% YoY)
Net Profit: ₹16,258 Cr (↓ 1.3% YoY due to higher provisions)
EPS: ₹21.23 (↓ 2.0% YoY)
Margin: 12.2% vs. 14.1% YoY
Provisions: ₹15,313 Cr (↑ 387% YoY, largely due to one-off items)
GNPA: 1.4% vs. 1.33% YoY
📂 Subsidiary & Associate Contributions
💰 Cost Structure – Q1 FY26
📅 FY26 and Long-Term Estimates
📈 Valuation Range Estimates
CMP ₹1,992 – near FY26 fair value.
⚖️ Portfolio Weightage
Suggested 3.97%/5% allocation as per current valuations in a diversified portfolio, given HDFC Bank’s consistent track record, strong moat, and stable asset quality.
✅ Conclusion – Risk & Reward Balance
Positives:
Market leader in advances & deposits among private banks
Strong subsidiaries in insurance, AMC, and NBFC adding to earnings
Low GNPA ratio and consistent RoE track record
Merger synergies to enhance cross-selling and balance sheet strength
Risks:
Near-term pressure on margins due to merger integration costs
Elevated provisions impacting short-term profitability
Competitive intensity in retail and SME lending
Regulatory changes in banking & financial services
📌 Investor View: Ideal for long-term compounding; SIP accumulation recommended during consolidation phases.
📢 Disclosure
This blog is for educational purposes only. Data is based on publicly available financials and reasonable assumptions, not an investment recommendation.
